Gear
Train Application (continued)
|
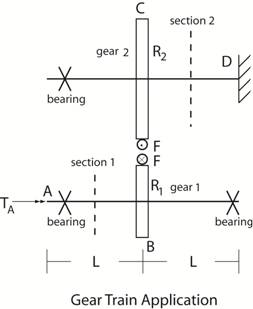
Step 3: Calculate Shaft
Torques: (repeated for clarity) Now T1 = R1
F, so
F = T1 / R1 = TA
/ R1 . (Torque in Shaft 1) So T2 = R2 F
= TA (R2
/ R1)
(Torque in Shaft 2) In general: angle
of twist = φ =
T L / J G where T = torque in shaft, L = length of shaft, J = polar moment of inertia of shaft and
G = shearing modulus of elasticity |
|
Step 4: Calculate rotation of
gear 2 relative to the fixed end of shaft 2, D. φC/D =
T2 L / J G = [TA (R2 / R1)
L] / J G where J
= π d4/32 |
|
For continuity between gears: R2 φC/D = R1
φ gear 1 (The displacements must be equal.) So φ gear 1 = (
R2 / R1 ) [TA (R2 / R1)
L] / J G = [TA (R2 / R1)2
L] / J G |
|
Step 5: Calculate φA/B:
Here: φA/B = T1
L / J G = TA L / J G Click here to continue
with this example. |
| Return to Notes on Solid Mechanics |
|---|
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.