Centrifugal Pumps
|
Example:
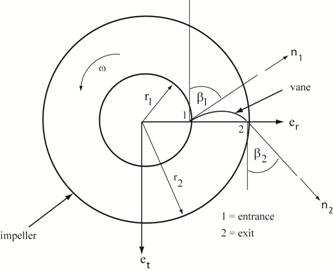
A centrifugal pump with r1 = 1/3 ft,
r2 = 1/2 ft, b1
= b2 = 1/6 ft, β2
= 30o rotates
counterclockwise at ω = 200 rad/sec as shown
in the figure below. The flowrate, Q, is 10 ft3/sec. Find
the angle at the leading edge of the vane,
β1, the torque,
T, driving the pump, the power added
to the fluid, P, the head, H, added to the fluid, and the pressure rise,
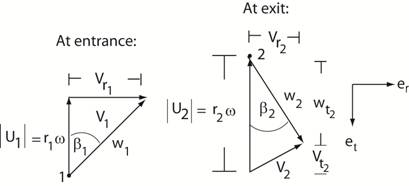
∆P, for the pump. Strategy: First plot the vector diagrams showing the
velocity vectors at the leading edge of the vane
and at the trailing edge of the vane.
Then apply the principles of conservation of mass, conservation
of angular momentum, and conservation of energy to solve for the requested information.
Click
here to continue with this example.
|
All rights reserved.