Equilibrium of a Particle
|
||
|
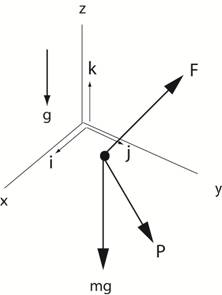
The figure below shows a
FBD of a particle of mass, m, acted on by three external forces including F,
P,
and the gravitational force (the weight of the particle, ˗ mg k . So for equilibrium of the
particle F + P +
mg(-k) = 0 where F = Fx i + Fy j + Fz
k and P = Px i + Py j + Pz
k Therefore Fx + Px = 0,
Fy + Py = 0,
Fz + Pz - mg
= 0 for equilibrium (result) |
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.