Combining Forms of Plane
Potential Flows
|
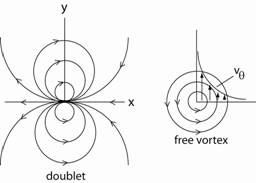
In a Nutshell: Each potential function satisfies the Laplace
equation (a linear equation). Thus the sum
of different potential functions also satisfies the Laplace equation and
represents a form of potential
flow. The table below lists basic,
plane potential functions that can be combined to form differing
flows.
|
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.