General
Equilibrium Problems Click
here for Strategy
|
||
|
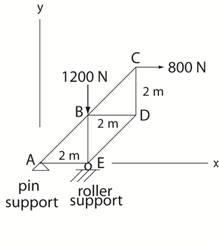
Example: Consider the truss ABCDE
acted on by a vertical load of 1200 N and a horizontal load
of 800 N and supported by a pin and roller. (Truss is a pin-connected
structure with forces acting only at pin locations.) |
||
|
In order to establish
equilibrium, the first step is to identify all forces acting on the truss. Start by constructing a
FBD of truss ABCDE to determine the support reactions. Click here to continue
with this example. |
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.