|
|
Key Concepts: A
fluid is a substance that cannot sustain a shear stress, no matter how
small,
without
deforming. Fluids may be liquids or
gases.
|
|
Liquids
i.e. water, oil, molasses
|
Gases
i.e. air, oxygen, nitrogen |
|
Liquids are nearly
incompressible
ρ
= constant
ρ = mass density |
Gases are compressible
"Ideal Gas Law"
p = ρ R T
p = absolute pressure
ρ = mass density
R = universal gas constant
T = absolute temperature
|
Common Properties of Fluids
|
Density
= mass /volume
|
Symbol
= ρ |
Value
for water = 1.94 slugs/ft3
= 1000 kg/m3 |
|
Specific
weight = weight/ volume
|
Symbol
= γ |
Value
for water = 62.4 lb/ft3
= 9800 N/m3 |
|
Specific
gravity = density of fluid/
density
of water
|
Symbol
= SG |
Value
for water = 1.0
Value
for oil = 0.9 |
Measurement of
Fluid Pressure (lb/ft2, N/m2, lb/in2, N/mm2): absolute pressure or gage pressure
absolute
pressure = atmospheric pressure + gage pressure
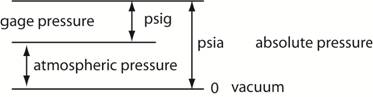
Example: Tire pressure is typically 35 psig
= (35 + 14.7) = 49.7 psia
|
