Pressure
Vessels
|
Example: The cylindrical, steel tank shown below is under a gage pressure of
1.5 MPa.† Its inner diameter is 750 mm with a
wall thickness of 9 mm.† The seams
forming the tank using butt welds are at an angle
of† θ with the longitudinal axis
of the tank.† Determine the normal stress perpendicular to the weld
and the shearing stress parallel to the weld for† θ = 60o. †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††††††††††††††††††††††† |
|
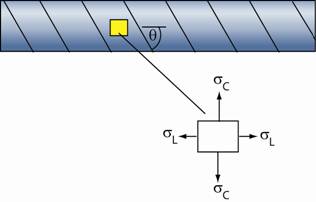
Strategy:† Use the expression† σC = pr/t and σL
= pr/2t to determine the circumferential and longitudinal, normal
components of stress on an element oriented along the cylinder as shown below.† Then use Mohrís circle to find the
components of stress for an element oriented along and perpendicular to the weld
seam. †††††††††††††††††††††††††† σC = †pr/t††
=† (1.5)(375)/9† =†
62.5 MPa σL = †pr/2t†
=† (1.5)(375)/(2)(9) = 31.25 MPa Next construct Mohrís
Circle for this element in plane stress. Use it to determine the
normal and shearing stresses on the face of an element rotated so that a face of the
element aligns with the weld.† Remember
that rotation of an element through an angle† θ†
is equivalent to rotation through an angle† 2θ on Mohrís Circle with both rotations in the same
direction. Click here to continue
with this example. |
| Return to Notes on Solid Mechanics |
|---|
All rights reserved.