Example - Analysis of Trusses using the Method of
Sections - (continued)
|
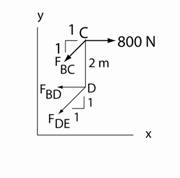
The FBD of the “cut” section is: Note that the “cut” passes through truss members BC, BD, and DE for which the forces are unknown. Also, note there are three equations of equilibrium available. So this application is determinate. If we first sum moments about joint D, then we will find the force in truss member BC. Σ MD = 0 taking counterclockwise as positive yields FBC (1/√2) (2) - 800 (2) = 0 So FBC = 800 √ 2 N. (tension) Next sum forces in the y-direction taking –y (downward) as positive. Σ Fy = 0 FBC (1/√ 2) + FDE (1/√ 2) = 0 which gives FDE = - FBC So FDE = - 800 √ 2 N. (compression) Note the forces in truss members BC and DE are equal in magnitude. Finally sum forces in the x-direction taking the x-direction as positive. Σ Fx = 0 (sum forces in the positive x-direction) which gives -FBD + 800 - 800 √ 2 (1/√ 2) + 800 √ 2 (1/√ 2) = 0 or FBD = 800 N (tension)
|
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.