Shear Flow in
Thin-walled Members (continued)
|
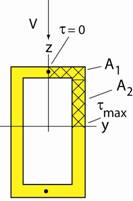
Next calculate the maximum
shear stress developed in the web. In
this case break the Q = A1
y1bar + A2 y2bar
Q for τmax is: Q = (Area)(ybar
for area about n.a.) = (100)(20)(140) + (130)(20)(65) Q =
4.49 x 105 mm3 So the maximum shear
stress in the web is (100)( 4.49 x 105)
/ (2.157 x 108)(20) = 10.4 MPa Note: The average shear stress in the web is the
shear force divided by the area of the web. Area of web =
(2)(260)(20) = 10400 mm2 τmax is: 100000/10400 =
9.62 MPa Note
that the average shear stress in the web provides a reasonable estimate of
the maximum shear stress developed in the web using VQ/It for
thin-walled closed sections undergoing shear. |
| Return to Notes on Solid Mechanics |
|---|
All rights reserved.