Dirichlet Applications - Heat Conduction in a
Plate (continued)
|
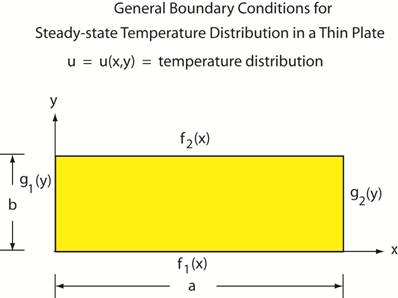
A complicated case exists when each edge has a nonhomogeneous boundary condition. i.e. u(x,0) = f1(x), u(x,b) = f2(x) ( 0 < x < a ) and u(0,y) = g1(y), u(a,y) = g2(y) (0 < y < b ) See the figure below.
In each case the equation for steady state heat conduction is uxx + uyy = 0 . |
||||
|
Strategy: Split the original problem into four problems each with one nonhomogeneous boundary condition as in the table below. Then use separation of variables for each problem. The sum of the four solutions is then the solution of the original problem. |
||||
|
|
||||
|
The general solution, u(x,y), for this complicated case is then: u(x,y) = u1(x,y) + u2(x,y) + u3(x,y) + u4(x,y) Click here to continue this discussion. |
Copyright © 2017 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.