Related Rate
Applications Click here to skip
to Optimization
|
In a nut shell: Relate rate problems
typically involve word problems where you are |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
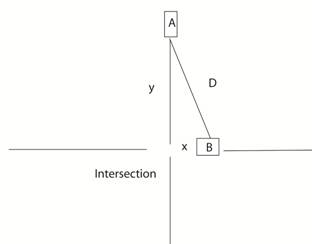
Example: Two cars are traveling towards an
intersection. Car A is
heading due south at 50 mph and is 0.5 miles
from the intersection. Car B is
heading due west at 40 mph and is 0.25 miles from the
intersection. Find the rate of change
of the distance between the two cars at this
instant. Apply the Pythagorean
theorem to unknown distance, D (hypoteneuse) in general terms. D =
√ ( x2 + y2 ) then use implicit differentiation dD/dt = ˝ ( x2 + y2
) -1/2 [ 2x dxdt + 2y
dy/dt ] Put in given values: x = 0.25,
y = 0.5, dy/dt = - 50, dx/dt = - 40 Then dD/dt = -62.6
mph
Click here for two other examples. |
| Return to Notes for Calculus 1 |
All rights reserved.