Numerical
Integration Example using Right Endpoint for Riemann Sum
|
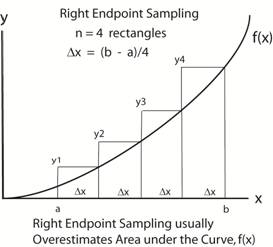
Estimate the area under
the curve, y(x) = x2
, from a
= 1 to
b = 3 . Note
for this increasing function, the right endpoint Riemann Sum overestimates the area. |
|
|
|
Note: The approximate
area =
( y1 + y2
+ y3 + y4
) Δx Here b
= 3, a
= 1, n
= 4 so
Δx
= (3 – 1)/4 =
0.5 Here
xi = a
+ i Δx x1 = 1.5, x2 = 2.0, x3 = 2.5, x3 = 3.0 y1 =
2.25, y2 =
4, y3 =
6.25, and y4= 9 |
|
Approximate area =
( 2.25 + 4 +
6.5 + 9 ) 0.5 = 10.875 Click here to use the
Riemann Sum to calculate the exact area. |
| Return to Notes for Calculus 1 |
All rights reserved.