Calculation of Pressure
Forces on Submerged Rectangular Plates (continued)
|
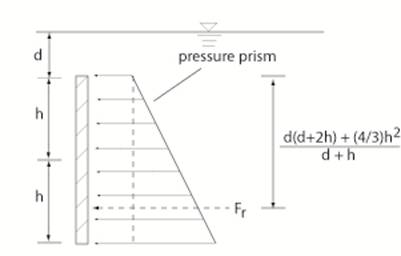
Case 3: Calculation of Pressure Forces on a
Vertical submerged plate The
magnitude of the pressure force
equals the pressure at the centroid of the plate times the area of
the plate. Let
γ be the specific weight
of the fluid. In this case the pressure
at the centroid of the plate is γ ( d + h ) . Let
w be the width of the plate (into the paper).
So the total pressure force Fr on the plate is [ γ ( d + h ) ] (2hw). The location of the pressure force is at the “centroid”
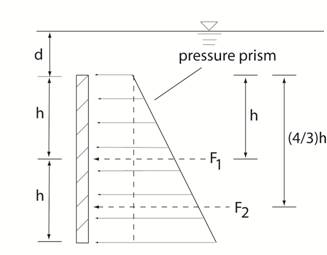
of the pressure prism, which in this case is a trapezoid. An alternate approach is to break the
trapezoidal pressure distribution into two parts. The first part is a uniform pressure
distribution of γd
and a triangular distribution starting from zero and increasing to γ
(2h). See the figure below. F1 = γ d ( 2hw ) and
F2 = γ h ( 2hw ) The location of each individual pressure force acts at the
“centroid” of its pressure prism. So F1 acts at the centroid of the rectangle. F2 acts at the centroid of the triangle. Notice, the strategy in each case to
calculate the resultant pressure force on a plate submerged in a fluid is the
same. The same strategy applies to a
“slanted” plate submerged in a fluid. |
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.