The Bernoulli Equation (continued)
|
Σ
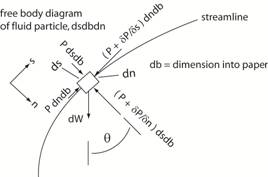
Fs = dm as P dn
db - (P + ∂P/∂s ds) dn
db – dW sin θ
= dm v dv/ds Now dm
= ρ dndbds and dW
= γ dndbds = ρg dndbds - (∂P/∂s) dn
db ds - ρg dndbds sin θ
= ρ dndbds v dv/ds By
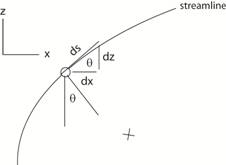
geometry from the figure below sin
θ = dz/ds
So - (∂P/∂s) dn db ds - ρg dndbds (dz/ds) = ρ dndbds v dv/ds - ∂P/∂s - ρg dz/ds =
ρ v dv/ds or ∂P
+ ρ v dv + ρg dz = 0 Integration of this equation gives the
Bernoulli equation:
where P = static pressure at point on streamline, ρ = mass density of fluid, g = acceleration of gravity, V
= speed of fluid at point on streamline, z = elevation at point on streamline |
Copyright © 2019 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.