Mohrís
Circle - Stress
|
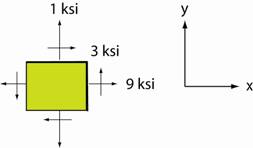
Example:† The element shown below
has the following stresses acting on its faces. †††† σx †=† 9 ksi,†† σy† =† 1 ksi,†† τxy =†
3 ksi.†
Construct Mohrís Circle.†
Determine the maximum and minimum normal
stresses and the maximum shear stress.†
Find the angle of the plane on which the
maximum shear stress acts and show the element. †††††††††††† †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† ††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† |
|
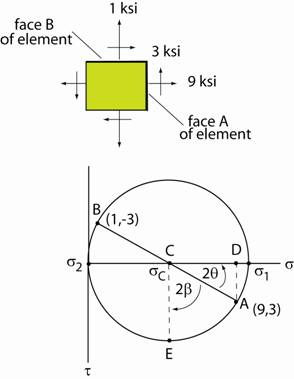
Strategy:† Identify face A and face B on
the element.† Construct Mohrís
Circle.† Rotate from plane A to determine the angle
of the plane on which the maximum shear stress occurs. The center of the circle
is at† σC =† (σx
+ σy)/2 = 9 + 1)/2† =† 5† and† τxy = 0. Plot point A and the
center of the circle.† From the figure
below determine the radius. ††††††††††††††††††††††††††† †††††††††††††††††††††††††††† Use triangle ADC in Mohrís
Circle.† AD = 3,† CD = 9 Ė 5 = 4† Therefore†
CA = 5 ksi Also† tan (2θ) = ĺ† so†
2θ = 36.9o†
and† 2β = 53.1o
.† Recall rotation of on Mohrís Circle is twice that on the
element. Click here to continue
with this example. |
| Return to Notes on Solid Mechanics |
|---|
All rights reserved.