Double
Integration using Cartesian Coordinates
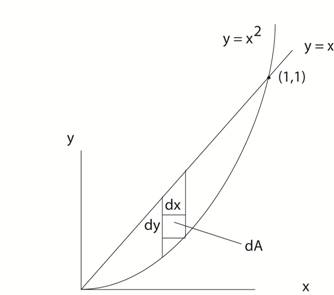
The curve y = x2 lies below y = x. The points of intersection are determined by x = x2 So x = 0 and x = 1 Now the element of area is dA where dA = dx dy = dy dx For the element shown above, choose to integrate on the variable y first. i.e. Sweep in the “y-direction first. So dA = dy dx and the integral becomes: x =1 y = x x =1 x A = ∫ ∫ dy dx = ∫ y | dx x = 0 y = x2 x = 0 x2 x =1 1 A = ∫ [ x - x2 ] dx = [ (1/2) x2 - (1/3) x3 ] | = 1/6 x = 0 0 Click here for another example. |
Copyright © 2017 Richard C. Coddington
All rights reserved.